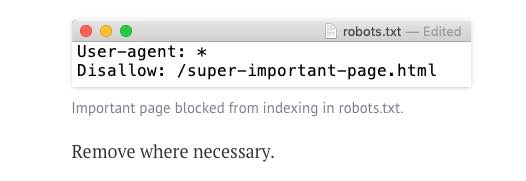
A Marketing Guide to How Keyword Stemming Works for SEO *
Keyword Stuffing Used to be the Norm
Content writing years ago was much different than it is today. Stuffing as many keywords as possible into your content was what everybody did. The following type of sentence was the standard. “Orlando Eye is one of many things to do near Orlando.” Sometimes we’d spell “Orando” or another word incorrectly to account for common typos.

When stuffing, writers might include five different variations of “things to do near Orlando” in a 300 word article. Keyword stuffing was encouraged by how search engines handled search queries. Content writers tried to duplicate the exact phrases or wording that people might search for. Then they used Google to help people find them.
However, Google progressed, as did marketers and content writers. Today, you barely have to think about SEO when crafting an article. If you’re a solid writer and you’re staying on-topic, it gets you there naturally when it comes to Search Engine Optimization.

Google has become awesome at reading and analyzing text. In the last decade it’s as if Google has gone from kindergarten to graduating from college. If you want to optimize your content for “kayaking near Orlando” it’s much easier today. Google understands that “kayaking springs near Orlando” and “kayaking tours near Orlando” are basically asking for the same thing. You no longer have to match keywords word-for-word. Don’t stuff your keywords, because that will result in low-quality articles, and Google hates bad content.
What is Keyword Stemming?
Google’s algorithms developed the ability to understand different forms of a keyword or phrase. This is called “keyword stemming,” stemming takes the root of a word (the stem) and determines what variations of the word deliver the information appropriate to the seach query.
If the stem word is “kayak” Google would recognize kayaking with manatees, kayaking orlando, kayak rentals near me and many other variations on that theme. Google recognizes the variations in addition to the stem word.

Stemming has been a developing concept at Google for many years. What has changed is how Google has become better at understanding word variations and how they are used. Because Google seach has evolved it is no longer necessary to stuff your content with word-for-word keyword matches.
Here’s a great article on how to succeed doing local SEO.
Google is Great for Keyword Suggestions
For most people the simplest solution is the free option available using Google. Entering your keyword into Google, it will automatically populate with suggestions. You may not want to use any of Google’s suggestions, however they may provide you with some pretty good ideas. For “hiking in Florida,” this is what Google comes up with:

Their suggestions are nothing I don’t already know. However, when I click on a search result and scroll to the bottom, I get helpful suggestions like “hiking in florida everglades” and “hiking in Florida with dogs.”
How You Can Find Keyword Variations
It’s second nature for many of us to write using stem word variations, and it’s easy to see a sentence that needs to be tweaked for optimization.
As an example, let’s optimize the last sentence for “keyword stemming.” Keyword stemming is second nature for many of us, and I can easily spot a sentence to tweak for optimization.
To find these keyword variations there are many tools that are available. Doing this is different than doing SEO research. If you already have an idea what keyword or phrase you want to optimize for, you just need to find it’s variations.
The following tools will help you create a list of variations. However, the best thing to do is to train yourself to think in keyword variations so it comes to you naturally.
Karooya Keyword Variation Tool
The simplest keyword variation tool is from Karooya. It’s a stripped down search tool that gives you straightforward variations, nothing more. Use it if your brain is stuck and you can’t think of common forms of single words.

SEMrush Keyword Magic Tool
The Keyword Magic Tool from SEMrush lets you enter a seed keyword (the stem) and generate more keyword ideas. I entered “kayaking in Florida” and selected “Broad Match,” which gives any variation of the phrase in any order. Here are the results:

Several of the variations still have “kayaking in Florida” written exactly like that, and I already know I can use that phrase as-is. What’s helpful are the suggestions for “best kayaking in Florida,” “best places to kayak in Florida” and “kayaking in Clearwater Florida.”
Ubersuggest Keyword Ideas
Neil Patel’s browser-based app Ubersuggest can give you keyword ideas from a stem word or phrase, and also tell you your chances of ranking for the keyword, plus the top search engine results.

Updating Your Content for Optimization
If your content isn’t optimized there’s a quick way to optimize. Seek out partial keyword phrases and update the sentence to maximize the SEO possibilities. For example, if I want to rank for “keyword stemming” I would search for “stemming” to find sentences where I didn’t use the full phrase. If I found one like: “Stemming isn’t new to Google.” I’d simply add “keyword” to the beginning of the sentence and boom, a bit more optimization.
Here’s another example. Let’s say I want to optimize for “biking in New York City.” If my original sentence is, “The best biking routes run along the river.” I can easily change it to any of these options:
- The best biking in New York City is along the river.
- New York City biking is prettiest along the river at sunrise.
- Check out these riverside biking routes in New York City.
I’ve optimized for my keyword and can also experiment with stemming if other variations fit better.
When Not to Use Keyword Stemming
Are there times that you would not want to use keyword stemming? It’s important to keep your keywords in sync with the context of your article. Also avoid overusing or misusing keyword stemming because you can create low-quality content that tries to trick Google and disappoints readers. Here are two examples:
- If I want to rank for “hiking in New York,” Google may recognize “hiker in New York,” but that’s not the context of my article. I’m not talking about hikers, I’m covering hiking trails. This variation doesn’t fit the context of my article, and it may seem like a bait-and-switch to Google or my readers.
- “Hiking in NYC” may be a Google-friendly variation to “hiking in NY,” but it’s changed the stem word too much and it’s out of context with the article.
Don’t use keyword stemming if it doesn’t fit the context or if the variation is unrelated to the stem word.
Final Thoughts About Keyword Stemming
It’s important to know what Google hates because it’s very similar to what your readers will hate. Google serves the user, and its algorithm changes are all about creating a better user experience. It’s as if Google has done some audience research for you.
Google doesn’t like content that seems engineered or uses clumsy wording. Keyword stemming gives you the ability vary your wording and focus on your writing quality while including plenty of SEO.
Want to learn more about how Google ranks your web pages? Check out Elegant Themes Beginner’s Guide to Google’s 4 Most-Important Ranking Algorithms.